
This widely used method is based on a complex combination of role assignments, authorizations, and permissions. The goal is to provide users with access only to data that’s been deemed necessary for their roles within the organization. Role-based access control (RBAC): RBAC grants access based on defined business functions rather than the individual user’s identity.This model is common in government and military environments.

A central authority regulates access rights based on different security levels.
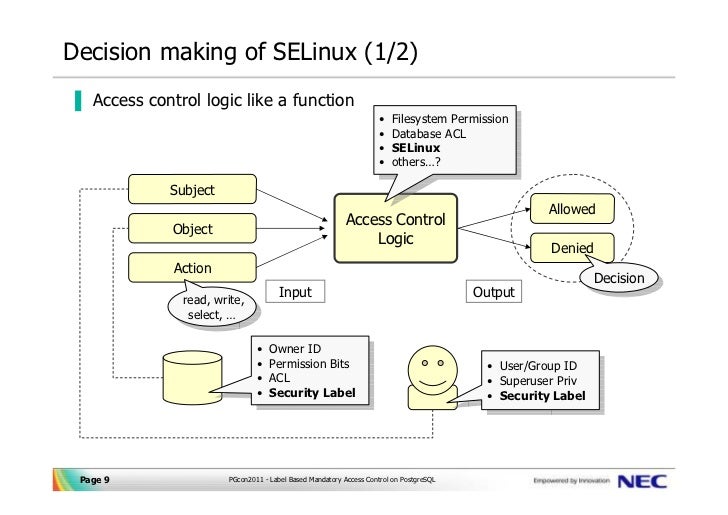
Mandatory access control (MAC): In this nondiscretionary model, people are granted access based on an information clearance. Discretionary access control (DAC): In this method, the owner or administrator of the protected system, data, or resource sets the policies for who is allowed access. Organizations typically choose the method that makes the most sense based on their unique security and compliance requirements. There are four main types of access control. Once a user is authenticated, access control then authorizes the appropriate level of access and allowed actions associated with that user’s credentials and IP address. All the three techniques have their drawbacks and benefits. The main types of access control include discretionary, mandatory and role based. Many access control systems also include multifactor authentication (MFA), a method that requires multiple authentication methods to verify a user’s identity. Access control models are security models whose purpose is to limit the activities of legitimate users. 
SQL Server includes securables at three different scopes: Server-scoped securables include such resources as logins, server roles, availability groups, endpoints, and databases as a whole. Access control identifies users by verifying various login credentials, which can include usernames and passwords, PINs, biometric scans, and security tokens. A securable is a specific SQL Server resource whose access is controlled by the database engine through the use of permissions.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
